As of 2021 there an estimated 3.6 Billion people connected through social media. That’s just about half the population of the entire world connected globally by the internet in the last 15 years.
That level of human connectivity has never happened before in history, and there’s no way it’s not having a massive effect on us both as individuals and as a collective group of inter-connected minds across the world.
But exactly how is social media affecting our individual consciousness?
And how is social media affecting our collective consciousness?
In this article we explore new studies, expert opinions, perspectives, and projections to gaina. Deeper understanding for how social media is re-shaping the digital world, our physical world, and our mental consciousness.
Let’s Dive In.
Social Media and Consciousness
To better understand how social media affects consciousness, first what is consciousness?

Describing what consciousness is sort of like describing the shape of water. Consciousness is so complex that even with today’s technology, scientists are still unsure of the origin of consciousness.
But origins aside, consciousness is generally defined as “the state of being aware”. It is also important to know that there are ‘levels of awareness’.
When we talk about social media affecting our consciousness, we’re talking about how it effects our mental state, awareness of our environments, and awareness of ourself.
The Effect Of Social Media On Individual Consciousness And How We Think As Individual Humans
What would life be like if we all lived in a world where everyone thinks the same? What if we could join groups of like-minded people, and just block out the thoughts of anyone who disagrees with us by pressing a button.
If all we saw in our experience of the world, was the same perspective, would we really have a deep understanding for how the world works? Or would we have a warped view of the actual reality?
Conscious vs. Sub-Conscious vs. Unconscious Effect of Social-Media –
Do you know the difference between consciousness and unconsciousness? Lets clarify the difference because social media has different effects on each.
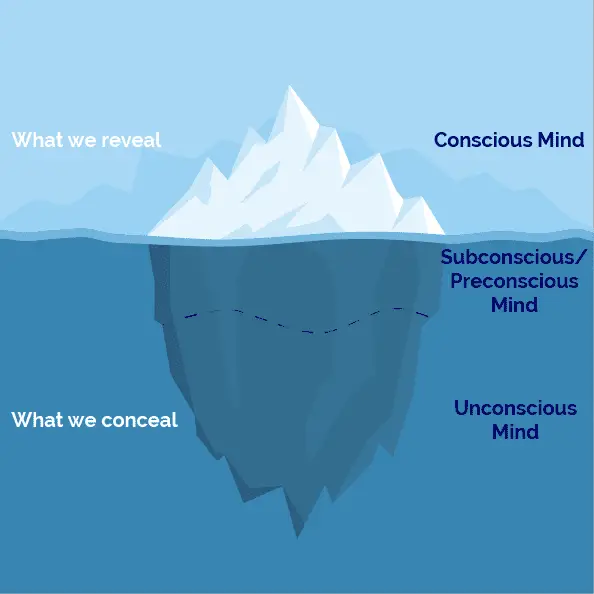
Conscious Mind –
Your conscious mind is everything you are aware of and thinking about right now. Your conscious mind is your awareness of the world around you.
For example, you might be consciously aware that you shouldn’t be scrolling on social media at work, but you do it anyway.
Sub-Conscious Mind –
Your sub-conscious mind (also known as pre-conscious) is like a huge storage bank. The subconscious mind contains information that you’re not currently thinking about, but that you can draw into your awareness with a conscious effort.
For example, when you do scroll on social media at work, you may be time yourself, but you’re also sub-consciously aware when you’ve spent way too much time not focusing on what you’re supposed to be focusing on.
Unconscious Mind –
The unconscious mind is made up from automatic process that the conscious mind cannot access because they happen underneath conscious awareness.
For example, the unconscious mind contains suppressed thoughts, feelings, and emotions which may effect everyday behavior with-out us being aware of it.
Another example would be developing a natural dislike for one political party or another after seeing a few dozen memes (whether they’re true or not). You may not even be able to remember where you got your opinion from, but unconsciously you’ve developed a strong dislike for someone or something.
Social Media May Interfere With Your Ability To Think Independently

If given two options to choose from, are you really thinking independently or are your options limited to give the illusion of choice?
With 50% of the world connected through social media, if you don’t understand the effect that its having on the masses, and on individual thoughts and ideas, then you’ll be subject to its effects unconsciously without knowing how or why.
As the grandfather of modern day psychology , Carl Jung, once said…,
“Until You Make The Unconscious Conscious, It Will Direct Your Life And You Will Call It Fate.“ –
Unconscious Biases –
If you haven’t heard the term “unconscious bias” before then you’re just like most people. Unconscious biases are “social stereotypes” that people form without even knowing it. According to diversity expert Dr. Renee Navarro, PharmD, MD, everyone holds unconscious beliefs, and these biases stem from our natural human tendency to organize social worlds by categorizing.

Unconscious bias IS NOT the same thing as conscious prejudice.
For example, as spread through social media, there’s lots of internet jokes about people named Kyle. It’s very possible that this could affect you (or already has) into unconsciously thinking a certain way about people named Kyle. When statistically speaking, you know just as little about a stranger named Kyle, as you do about a stranger named Tom.
Social media can deepen our unconscious bias if we’re not aware of it.
According op the “Unconscious Bias Training” page from University of California, biases, whether conscious or unconscious, are not limited to ethnicity and race (or the name Kyle).
Racial bias makes the most headlines, but biases can and do exist toward any social group.
The Mere Exposure Effect –
In psychology, the ‘mere exposure effect’ explains that, the more often people have been previously exposed to something, the more they like it.
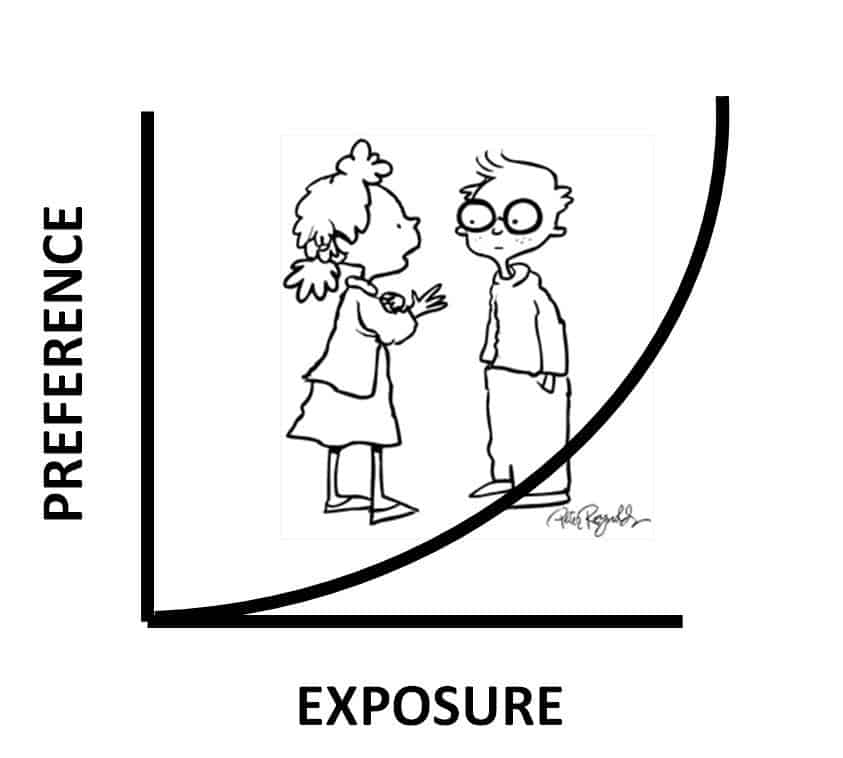

This is why “re-targeting” ads on social media (ads showing you products that you’ve seen before) are so prevalent and effective. Dr. Elizabeth Hopper explains that the “mere exposure effect” still works, even when people “DO NOT consciously remember” that they’ve seen the object (or product, or idea) before.
But the ‘mere exposure effect’ isn’t limited to liking and buying products on social media. The ‘mere exposure effect can also be used to convey ideas, thoughts, and manipulate opinions.
For example, negative political attacks on social media work (in part) because of the ‘mere exposure effect”. You may not agree (or even disagree) with the negative attack, but after repeated exposure to the same narrative and the same negative attack, you may start to unconsciously view that person in a negative light.
In 1968, social psychologist Dr. Robert Zajonc published one of the founding papers on “the mere exposure effect”. Dr. Zajonc found that, simply by being exposed to something on a repeated basis, it was enough to swing someone’s opinion.
Repeated exposure to the same ideas, products, and opinions on social media can warp our conscious awareness and understanding for our environments.
The Dunning-Kruger Effect –
The Dunning-Kruger effect gets it’s name from a famous 1999 study by Cornell University psychologists David Dunning and Justin Kruger.
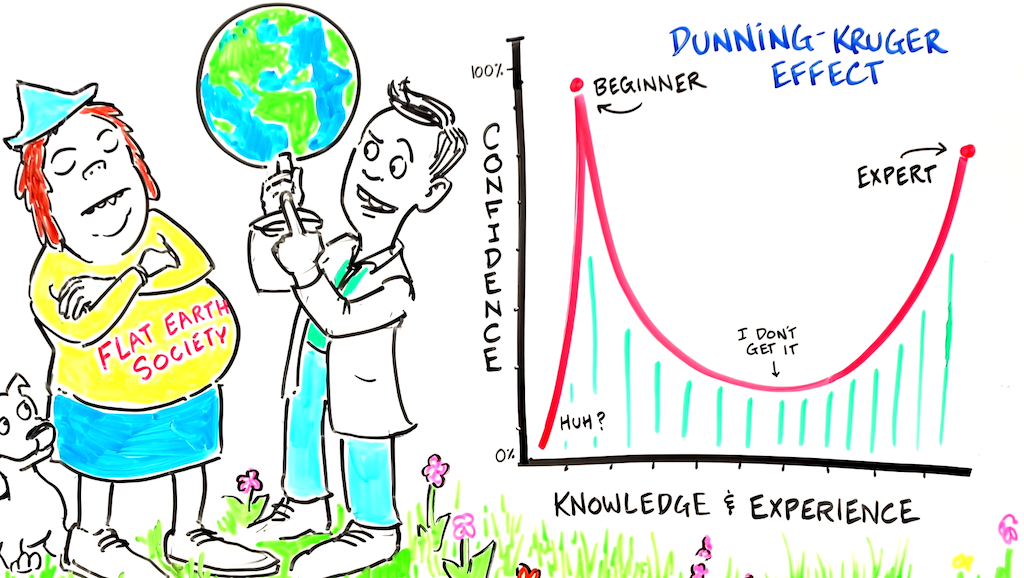
The Dunning-Kruger effect is a proven bias common in human nature. Dr. Dunning and Dr. Kruger found that the less someone knows about something, the more likely they are to overestimate how much they know. The same goes for ability.
Experts believe the “Dunning-Kruger Effect” occurs due to a lack of self-awareness preventing an accurate self-assessment. Other studies have shown that while most people think they are self-aware, only 10-15% are actually self-aware.
In the eyes of expert psychologist Dr. Joe Kort, social media consists of millions of people with lower self-awareness typing away as “trolls”, critics, conspiracy theorists, and online bullies. All of whom strongly believe their own opinion despite having no expertise, formal training, logical reasoning, or evidence to support their perspectives.
The “Dunning-Kruger Effect” leads people to believe they are experts in subjects that they know very little about.
Dr. Kort has noticed that on social media that some of these people go out of their way to attack and ridicule anyone who they disagree with. To them, their opinion is as valid (or even more so) than the expert’s opinion (who has gained years of knowledge and experience through work and research). They have done no research of their own, and yet after watching a short video, they present their opinion as an obvious fact.
As Aristotle was famously quoted saying…,
“The more you know, the more you know how little you know”. And the less you know, the more you think you know.
Groupthink –
Group think is when a collective group forms around a particular idea, belief, or thought, and anyone who disagrees risks being kicked out of the group.
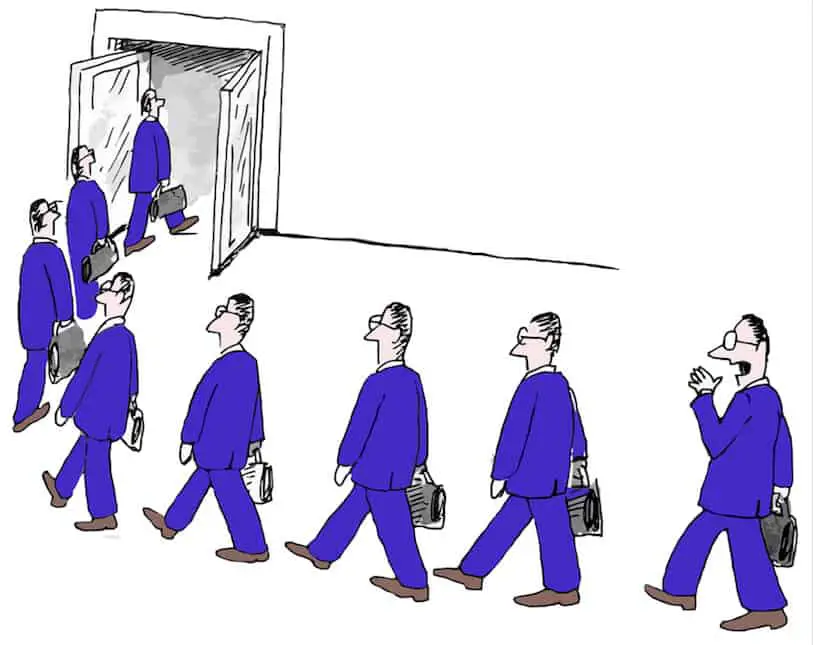
Group think can be very dangerous, because it creates an atmosphere where people just blindly follow the group with-out thinking for themselves. Social media groups (especially politically charged social media groups) are prime candidates for falling victim to groupthink.
Groupthink affects social skills and is associated with the psychology of a “herd mentality”.
For some people there’s safety in the herd. By joining a herd you can fit in easily and you don’t have to think for yourself. But also, if the front of the herd runs off a cliff, the rest follow. So in the end, thinking for oneself might be more difficult, and could risk being kicked out of the group, but ultimately it could save you from blindly running off a cliff.
Groupthink is a natural human trait that can be observed from small elementary school groups, all the way up to giant corporations, and even in large governments.
No-one is immune from falling victim to groupthink.
Populism also goes hand-in-hand with group think, as populism is when a group confuses what is popular for what is true.
The Anchoring Bias –
The anchoring bias is used heavily by news and media outlets to sway readers opinions, especially in headline writing.
The anchoring effect, or anchoring bias, is a natural psychological human tendency to rely on “initial information” to ‘anchor’ subsequent interpretations of the information that follows.
For example, I read a headline a few weeks ago that read something along the lines of “Marijuana Use Could Increase Chance of Getting Covid-19” After reading the article it turns out there was no correlation. But the anchoring text in the headline was being used to paint the picture of marijuana in a negative light.
CNN and Fox News also use the anchoring effect to subtly frame opposing political parties in a negative perspective. For example, “In clear disregard of democracy, Democrats …..” or “In obvious conflict with the constitution, Republicans….”
In both cases, what-ever wording comes next, it will be affected by the anchor text which frames the perspective of the reader for the rest of the article. Social media is the perfect breeding ground for unknowing users to fall victim to this type of manipulation by interested parties leveraging the anchoring bias in their favor.
Authority Bias –
The authority bias can unconsciously influence our behavior without us even being aware of it.

What is authority bias? Authority bias is a natural psychological tendency for humans to heavily weigh the opinion of an authority figure, regardless of any actual qualifications.
This is why politicians want celebrity endorsements. Because people listen to celebrities (and often worship celebrities) as authority figures, regardless of whether they understand (or are even qualified to understand) the inner workings of economics and geo-politics.
Social media is filled with authority figures (both real celebrities and fake guru’s) trying to sell us products and influence opinions. It’s our responsibility as social media consumers to be aware of the authority bias.
Just because Dwayne “the Rock” Johnson is on TV doesn’t mean he knows how to cook or understands the economic impacts of the stock market vs. interest rates. Yet his name is on cookbooks, and he is commonly asked political questions in interviews.
The Blind Spot Bias –
The blind spot bias is interesting because everyone (including you and me) is effected by it. The blind spot bias is a psychological defect in the human brain that leads us to identify bias’s in other people without recognizing our own bias’s.
In a recent study with 661 participants, all but 1 felt they were less bias than the average person. This is the blind spot bias in full effect.
When posting on social media, reading articles, and passing judgement, remember to check your blind-spot to see where you might be being bias. If you think you’re not bias at all, remember so does everyone else. Chances are you’re likely bias in one way or another (could be negative or positive bias)
What Social Media Is Really Doing To Your Brain
How The Internet May Be Changing Our Human Cognition –
The internet has only been publicly available for less than 30 years, and modern-day social media platforms are only 15 years old.
A new study published on the internet’s effect on our brain’s cognition has left researchers with much to be desired. The lead Author, Dr Joseph Firth, from University of Manchester concluded that…
“For better or for worse, we are already conducting a mass‐scale experiment of extensive Internet usage across the global population.”
Here are 9 key takeaways from the study
- The Internet is becoming highly proficient at capturing our attention
- Social Media is cultivating a global shift in how people gather information, and connect with one another
- The internet is encouraging us to engage in more “multi‐tasking” , rather than sustained focus
- Social Media is impacting our “real life” in unforeseen ways
- The long‐term effects of the internet & social media have yet to be established
- The internet is having adverse effects on attention in early adolescence
- Higher frequency Internet use in children over 3 is linked with decreased verbal intelligence
- Internet use could actually help older adults to maintain cognitive function throughout old age
- Older adults may be able to harness social media in order to overcome isolation.
Is Social Media Addictive? –
Yes. A study conducted by the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at the University of Missouri found that up to 10% of all Internet users show sign of internet dependency.

Are you addicted to the internet? Find Out…
According to Dr. Doraiswamy, a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Duke University Medical Center…
“Brain imaging studies show that compulsive Internet use may induce changes in some brain reward pathways that are similar to that seen in drug addiction,”
The Science Behind The Social Media Addiction –

Social scientists believe that “the ease of access to social media” (it’s in your pocket at all times) creates a constant competition for your attention.
Social media and the internet draw in our attention with the constant promise of new content, new updates, and new information.
According to Harvard- and Johns Hopkins-trained neurologist and neuroscientist, Dr. Majid Fotuhi – “Heavy social media users become less able to ignore distraction in general. Not only does this lead to poorer cognitive performance, but it shrinks parts of the brain associated with maintaining attention.”
Similar to clay, the human brain is malleable. Our brain neurons are constantly adapting, changing, making new connections, and releasing old connections. Therefore we can learn new tasks, new skills, learn new information, and form habits. This ability for our brains to adapt and change is called “Neuroplasticity”.
And Neuroplasticity has a big effect on our attention, memory, and cognitive function.
Changes In Your Brains Reward System (Dopamine) –
Who’s up for a little ‘hit’ of dopamine?

Dopamine is the chemical in our brain that gives us pleasure. When we see an old friend, score a game winning goal, have sex, smoke crack, or get a “like” on Facebook, our brain releases dopamine as a positive reward. Smoking crack releases an ocean of dopamine which is why it’s so addictive. But getting like on social media also releases a little bit of dopamine, and the more likes, the more dopamine.
Through neuroplasticity, you’re brain will slowly learn to expect a reward of dopamine every time you pick up your phone.
Social media makes us addicted to screens. It provides us an immediate reward in the form of a dopamine release (the happy hormone) every time you post or get a notification from an app.
According to “NeuroGrow Brain Fitness Center”, constantly scrolling and looking at a screen rewires your brain to want more of what caused that dopamine release. More likes, more funny memes, more content. This subtle subconscious craving is exactly what leads us to social media addiction.
“Studies show that the brain scans of heavy social media users look very similar to those addicted to drugs or gambling.”
Controlling Social Media & Internet Addiction –

Have you found yourself mindlessly scrolling through your social media timeline. Doing what? Maybe you just went to check the time and next thing you know you’ve been on Instagram for 20 minutes.
You’re not alone though. And fortunately, there’s some real easy tips to improve your awareness of your social media use.
First, Understand Why You’re Using Social Media.
Why are you logging in? Why are you reaching for your phone?
Are you bored, anxious, or nervous? Are you looking up a co-worker? Are you posting something to prove a point? Are you spying on a friend? Are you posting for attention?
Did you mean to look at something else and get distracted?
Whatever your reason is, it’s important that you understand why you’re using social media.
Here’s a guide wrote that you might find helpful – 38 Tips To Help You Use Social Media More Consciously
Be Mindful Of Why You’re Scrolling

Once you’re on social media, the human brain is easily susceptible to distractions. And social media companies understand this psychological vulnerability. Social media companies make money by showing us engaging content that captures our attention.
Logging into social media with a “primary objective” is like walking by a circus with-out trying to look.
As soon as you log in, you’re bombarded with videos and photos specifically tailored to match your psychological profile for maximum engagement.
With-in seconds you forgot why you logged in to begin with and are now mindlessly scrolling. STOP
Be mindful of why you’re scrolling and what your primary objective is.
Social Media and Digital Collective Consciousness
What is collective consciousness ?
The Collective Consciousness, is the shared beliefs, ideas, knowledge, morals, values, and attitudes common among a group, community, entire population, or species.

In the days of our ancient caveman ancestors, collective consciousness and knowledge could only be shared between small cave-dwelling groups. As our species evolved the collective consciousness grew as hunter gathers settled into collective tribes, and as ancient cities and civilizations expanded.
As technology advanced and communication expanded through-out the ages from the telegraph, to the telephone, radio, television, internet, and now social media, the collective consciousness has expanded as well.
Currently, us humans are the most connected we’ve ever been in known human history. Through social media, our collective human experiences are shared millions (if not billions) of times everyday.
The internet has become the storage place for our collective consciousness with its capacity to influence individual minds, and unify our experiences.
Social Media As The Strongest Medium To Shape Collective Consciousness
With so many people connect through social media, it can have steep consequences (positive and negative).
Potential Negative Effects of the Collective Consciousness on Social Media –

Due to natural vulnerabilities in human psychology (outlined above) social media is a great place to manipulate and influence popular opinion.
False information can spread to millions of people in seconds. New technology can manipulate photos, videos, and voices to spread mis-leading “agenda driven” information with the intent to sway popular understanding and popular opinion.
Positive Effects of the Collective Consciousness on Social Media –

Social media can connect people like never before. Ultimately, it’s my belief that human nature is ‘by-in-large’ positive and kind. If most people, see an old lady struggling to carry something they will help out of pure good will.
Social media has helped connect people in need with all sorts of things. New houses after fire damage, donations for water in Africa, support for foreign countries ravaged by war, and collective internet sleuths solving crimes which police forces don’t have the man power to dedicate to.
We Still Need Face-To-Face Contact.
At the end of the day the internet, social media, zoom calls, the Meta-verse, and the digital world in general are slowly taking up more and more space out of our regular human-human interactions.

An article written by the Indeed Editorial Team highlights trust as the number one factor in face to face communication vs. digital communication.
The indeed team has found that by communicating face-to-face it shows friends and colleagues that you have their best interests in mind. Person-person communication allows both parties to observe body language which has been found to represent at least 55% of total communication.
Communicating in person gives a much better glimpse into your personality as compared to communicating through social media or on zoom. Face-to-face interactions allows us to convey a specific ‘sincerity’ in both words and actions that can get missed when communicating through text only.
The result is a sense of trust, feel good transparency, and human connection.
Final Thoughts – How Does Social Media Affect Our Consciousness?
Social media is still new and the effects may not be truly known for decades to come.
Social media is clearly influencing our individual brains, mindset, and consciousness. The short-term effects seem to be clearly linked to our ability to focus, concentrate, interact in human form, and interpret information credibility.
The long-term individual effects are not so clear, but still present non-the less. As time moves on and as more long-term data becomes available the longer-term effects of social media will become more obvious.
From a higher perspective, the effects of social media on our collective human consciousness is having a huge impact in our societies politics, tribalism, and means of communication.
Going forward I’m hopeful that as a society we’ll be able to take more of the good brought on b social media, and ‘weed out’ more of the negative aspects of social media’s effect on our human consciousness.
Loved what you read?
Hit that share button and let the world in on the secret – we’d be thrilled!
Got thoughts? We’re all ears for your feedback, corrections, or a good old chat. Don’t be shy; drop us a line.
And hey, don’t miss out on our curated list of must-reads in the recommended books section.
Big thanks for diving in with us today!